In the U.S., the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) is the organization that develops the accounting standards and principles. Corporations whose stock is publicly traded must also comply with the reporting requirements of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), an agency of the U.S. government. Equity represents the net assets owned by the owners (the shareholders). For example, in Big Dog’s January 31 balance sheet, net assets are $12,000, calculated as total assets of $19,100 minus total liabilities of $7,100.
- These questions can be used as part of a discussion with other members of your class, or they can be used for your own self-assessment as you prepare for your graded assessments.
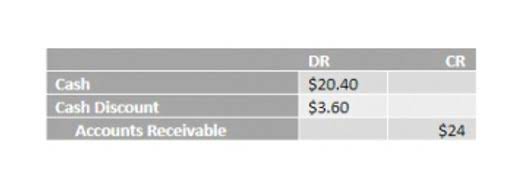
- Accountants track partial payments on debts and liabilities using the term “on credit” (or “on account”).
- All changes are summarized on the “bottom line” as net income, often reported as “net loss” when income is less than zero.
- Accounting information systems (AIS) use technology to collect, track, and store financial activity for accountants to use.
- In a world that demands transparency and accountability, financial statement disclosures serve to communicate the intricate details behind a company’s numbers.
A manufacturer’s financial reports may showcase products selling well and needing further production capacity. This data-driven decision making enhances the company’s credibility when seeking expansion of productive capacity. Regulators, whether government agencies, tax authorities, or industry watchdogs, play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of financial reporting. They ensure that companies adhere to standards and regulations to safeguard the interests of all stakeholders. The standard requires financial records to reproduce an economic reality “complete, neutral, and free from error.” At the heart of every financial accountant’s duties is presenting factual information. Income statements show how much the company earned and how much it spent.
Accounting Period
In addition to management using financial accounting to gain information on operations, the following groups use financial accounting reporting. The accrual method of financial accounting records transactions independently of cash usage. Revenue is recorded when it is earned (when a bill is sent), not when it actually arrives (when the bill is paid). Accrual accounting recognizes the impact of a transaction over a period of time. Financial accounting unfolds a clear picture of a company’s financial health, aids strategic decision-making, promotes regulatory compliance and allows for evaluation of financial performance. Its standardized methods and principles create an equitable platform for stakeholders, fostering trust in the economic landscape.
Financial accountants specializing in tax accounting can help when sales and other taxes come due. The book of transaction records relies on double entry accounting to drive data consistency. Use the same information EXCEPT assume that during the second year, additional shares were issued for cash of $3,000.
European Commission approves extension of film tax credit
Financial statements are the landmarks of the financial accounting roadmap. They serve as navigators communicating a company’s financial journey to the world. They may analyze financial ratios and trends to make informed decisions. This analysis helps us to understand whether the business is profitable financial accounting is often referred to as a and solvent, and to model future cash flows. External parties gauge the level of reliability they want to see, like a symphony’s audience can appreciate the work of the conductor and the orchestral performance. For example, a goods manufacturer will have a variety of sales and payment categories.
The Notes to Financial Statements, often referred to simply as “notes,” are an integral component of a company’s financial reports. They are a means of providing additional detail and explanation to the numbers presented in the formal financial statements. Notes are required by generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and international financial reporting standards (IFRS) to ensure a standard approach to transparency across different organizations. The key difference between financial and managerial accounting is that financial accounting provides information to external parties, while managerial accounting helps managers within the organization make decisions. Managerial accounting assesses financial performance and hopes to drive smarter decision-making through internal reports that analyze operations. An analysis includes evaluating the income statement to assess a company’s profitability and studying the balance sheet to evaluate financial health.
The Power of Financial Statements: Landmarks of the Financial Roadmap
Balance sheets capture what the company owns (assets), owes (liabilities), and what remains for the owners (retained earnings and equity accounts). A well-prepared balance sheet showcases the business’s financial stability and capital structure. It may include details sometimes found in a separate statement of retained earnings or shareholders’ equity statement. Revenues and expenses are accounted for and reported on the income statement, resulting in the determination of net income at the bottom of the statement.
Forensic accounting is a unique combination of accounting, auditing, and investigative techniques. Here are some of the different areas of accounting and what they entail. All users of our online services are subject to our Privacy Statement and agree to be bound by the Terms of Service. International companies follow International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), which is similar to GAAP in many ways but not all. The FASB and IASB have several initiatives to help bring the standards closer together.
